The Internet of Things (IoT) is the most impactful technological revolution
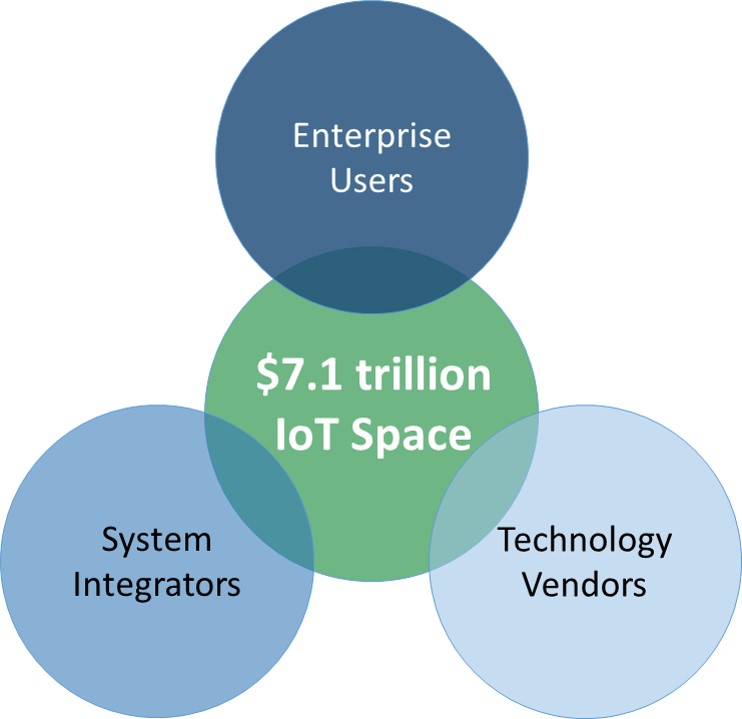
IoT market to hit $7.1 trillion by 2020: IDC
~100 billion sensors humming the planet in the near future integrated with most Vertical Industries.
Extremely efficient, real-time data collection and integration vital
Large Fortune 500 Organizations e.g GE and Intel are pivoting to become IoT and Big Data leaders.
$70 Billion spent annually on Big Data Integration and Data Quality Tools
Data complexity
Multi-Domain Extraction – Traditional, Social, Sensor’s both structured and unstructured.
Big Data Skill Shortage
5000+ enterprise customers currently have 3 or more Big Data technologies in their environments
Average IT budget: $1B/yr
30% focused on Big Data / Analytics
Bottom Line:
Largest potential market any way you slice it.
IoT Corporate End users, B2B and B2C; Top Global 2000 including the fortune 500.
On an average of $250 Million to $2 Billion for each, being allocated to align with big data cloud and IoT solutions.
Current Technology Vendors pivoting towards IoT.
Technology Vendors providing products and solutions to individuals, small businesses, commercial and large organizations whether it is component, hardware, devices, industrial equipment, home appliances, personal wearables etc. are all investing billions of dollars in R&D and aligning their businesses and investments to embrace the IoT opportunity.
System Integrators, based on their quarterly surveys, each of the top SIs; They have identified Big Data and IoT.
Significant investments are being made- an average of $1 Billion per System Integrator and 25-50 thousand personnel in each SI will be certified in cloud enabled IoT Solutions and services.
Browse the latest technical jobs that are available at Dragonfly. Find them here first. Learn More

Cognitive computing is an evolution of technology that attempts to make sense of a complex world that is drowning in data in all forms and shapes. Organizations standardized business processes and managed business data more efficiently and accurately than with manual methods. However, as the volume and diversity of data has increased exponentially, many organizations cannot turn that data into actionable knowledge. The amount of new information an individual needs to understand or analyze to make good decisions is overwhelming. The next generation of solutions combines some traditional technology techniques with innovations so that organizations can solve vexing problems.
A cognitive computing system consists of tools and techniques, including Big Data and analytics, machine learning, Internet of Things (IoT), Natural Language Processing(NLP), causal induction, probabilistic reasoning, and data visualization. Cognitive systems have the capability to learn, remember, provoke, analyze, and resolve in a manner that is contextually relevant to the organization or to the individual user.
Handle huge amount of data in many different forms and assimilate all sorts of data and knowledge that is available from a variety of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured sources
Analyze industry-specific data (typically unstructured) that is constantly expanding
Correlate a variety of data sources to determine context, patterns, and anomalies
Find a way to match the data with deep expertise
Analyze large amounts of data to support decision making, such as next best action
Build system which learn and change as business conditions change
Leverage highly distributed and cost-effective computing services to make large-scale cognitive computing operational
Process streaming data coming from equipment sensors to medical devices to temperature sensors to stock market financial data to video streams and IoT at high speeds. Streaming data is useful when analytics need to be done in real time while the data is in motion, because the value of the analysis (and often the data) decreases with time. For example, if you can’t analyze and act immediately, a sales opportunity might be lost or a threat might go undetected